It’s Lunar New Year and a cart full of goodies is being pushed through the hustle and bustle of a cramped Hong Kong street. In an instant, a mouth-watering smell rises into the air, drawing in hungry tummies as plates of fishballs exchange hands. A once common sight with as many as 50 000 hawkers and informal vendors plying their trade in the 1970s, Hong Kong now only boasts around 6 000 legally licensed food hawkers to cater to a hungry Hong Kong populace.
This community of itinerant hawkers or food peddlers infamously and affectionately referred to as the jau gwei (lit. running from ghosts) scatter in all directions as warning cries of approaching authorities fill the streets. Without official documentation, many jau gwei operate illegally with small carts which they push towards jostling markets and busy city intersections. Always on the hunt for their next sale, the jau gwei have long been considered a public nuisance by authorities seeking stricter regulations on the informal food market. Hygienic standards, noise pollution, and traffic congestion are some of the common bureaucratic buzzwords sparking controversy, especially as the jau gwei are seen as an authentic expression of working-class Hong Kong identity.

Fishball Riot 2016
Therefore, it is barely a surprise that attempts by city authorities – whether backed by the British Crown or mainland China – to regulate the jau gwei are viewed with distrust. Traditionally, caution rather than coercion has been the path to follow. However, since the early 2010s, authorities have stepped up their efforts at cracking down on the scene. In the politically charged atmosphere of Hong Kong, the fuse burned through once more in 2016, and culminated in the now infamous violent Mong Kok riot between localist groups and police forces. Heavily concerned with and informed by the notion of self-determination, the latter were quick to jump on the bandwagon to defend what they saw as an interference by mainland China to curb local culture.
The Mong Kok riot was striking for two of its features: first, for the use of violence and second, for the well-known plight of the jau gwei prior the violent outbreak. Two questions arise from these features: why were both sides prepared to fall back to the use violence, and why were the jau gwei worth fighting for or against in this particular instance?
The historical background is to be taken into account as a first instance to delimit the efforts of peaceful protest and its role in challenging the legitimization of the state. The path of Hong Kong identity thereafter gained leeway as an inherently political manifestation in challenging the legitimization of the state, and embedded the plight of the jau gwei within the context of this (re)configuration of Hong Kong identity in the greater pursuit of political representation. Importantly, Hong Kong identity in its particular (re)configuration(s) is taken as a naturally given process. The way of talking about this identity however is variable under the process of discourse, e.g. in the contemporary scope of Hong Kong society and its growing polarization and politicization.
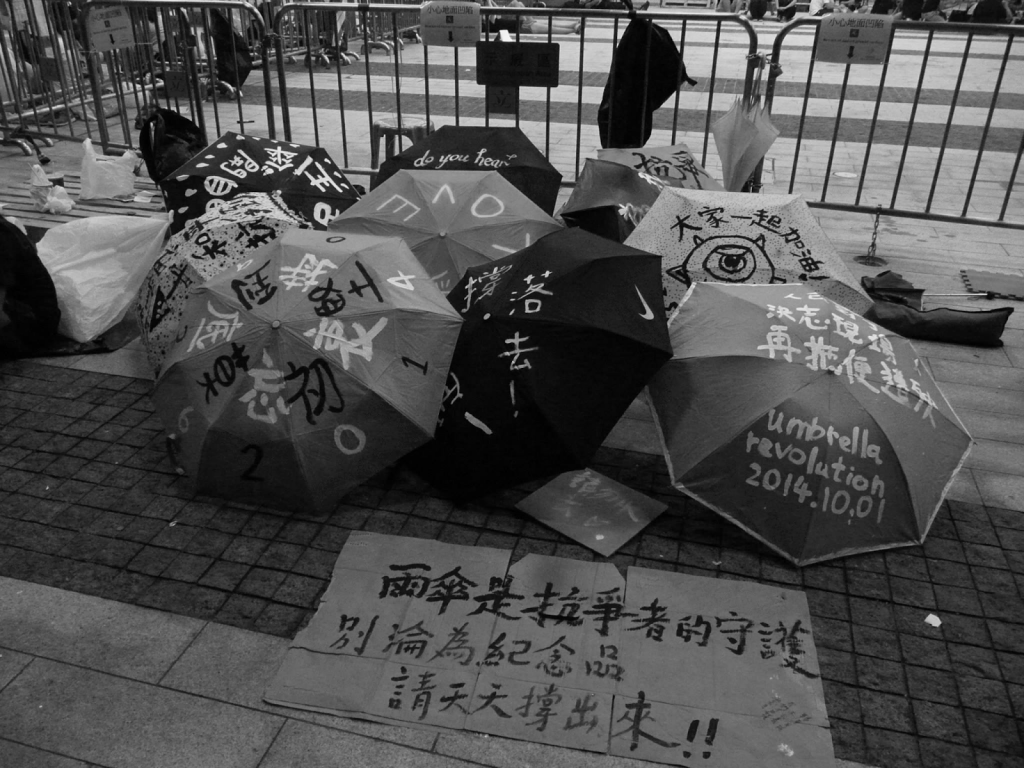

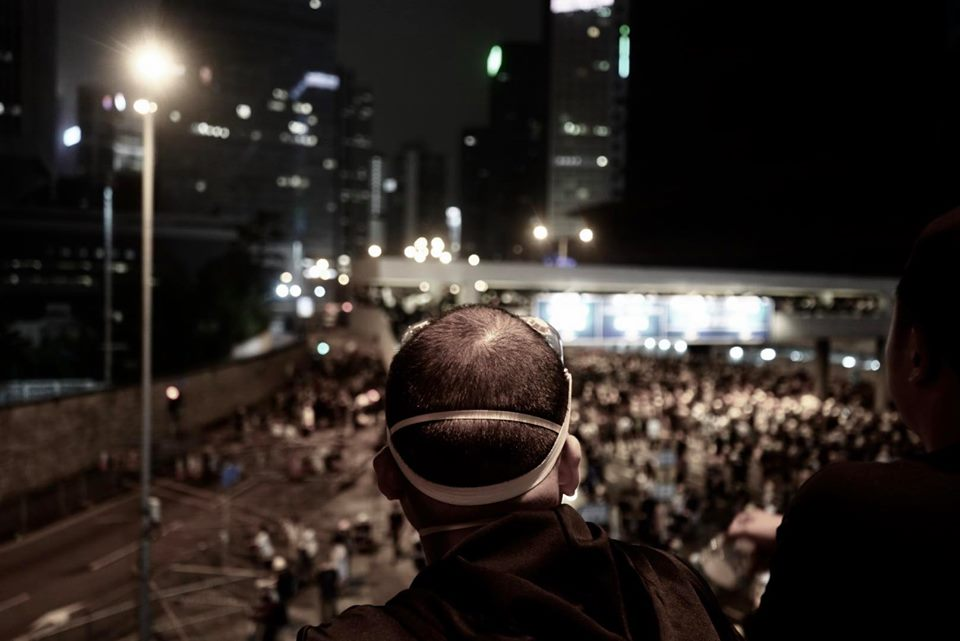
Umbrella Movement 2014
One can’t talk about this polarization without reference to the Umbrella Movement in 2014. In a nutshell, the Umbrella Movement sought by means of popular sentiment to protest for more – and especially fairer – representation in the government. The largely peaceful protests aimed at highlighting and proposing betterment to Hong Kong’s skewed political system ultimately fizzled out in disappointment as the Communist Party neither budged nor exhibited a willingness to engage, let alone negotiate, any solutions. Too high were the rulers and tycoon profiteers in their ivory tower to be touched by the people’s demands. Arguably, by sitting out the wave of discontent, the Communist Party showed its disregard for Hong Kong civil society. What was to be done to effect change?
Due to the resulting disappointment and disillusionment within Hong Kong society, new forms of questioning the authority arose and older ones such as localism or nativism once again gained traction. These groups aimed their sights at the “one nation, two systems” policy. The leading line of argumentation being: if there are two nations with two different sets of essentially different people, then this policy doesn’t work. The Mong Kok riot can be seen in this light, however, it doesn’t offer any clues as to why violence was used.
By means of understanding the resurgent electrification of Hong Kong politics, one must necessarily evaluate the role the jau gwei have been assigned to within it. As a group, which has its historical roots in mainland China yet is firmly embedded within contemporary Hong Kong culture as a space of shared memory, the jau gwei offer a unique green screen to project values, which I argue to be generationally all-encompassing.

Contested Identities
This all encompassing identity is notoriously difficult to pin with two generational camps pitted against each, namely the pro-independence youth versus the island’s elderly. Notably, the historical origins of the jau gwei and Hong Kong bureaucracy have both done their part in fostering a close link between the jau gwei and the (imagined) mainland, especially from an elderly perspective. After all, the jau gwei are descendents from impoverished Chinese mainlanders who sought to scrape a life in the former colony – that’s how the informal food market came into being. Generally, the jau gwei represent the opinions of the elderly mainlanders who prefer maintaining the status quo. In their opinion, retaining Hong Kong’s slight concessions in terms of freedom is considered infinitely better than risking it all for an uncertain outcome.
In addition, the jau gwei’s profession is strictly hereditary as stipulated by Hong Kong law and its licensing practices. These were put into place to restrict access to – and naturally ‘eradicate’ – the itinerant market in favour of tax-paying and state-building revenue opportunities. Attempts to squash the market underscores the ironic twist behind the story of the jau gwei: they are rooted in mainland culture but uprooted by its authority at the same. Keeping tabs with the status quo will not end their plight in the long run. Localists helping the jau gwei only fosters a sense of interdependence amongst Hong Kong citizens that prefer – more and more – the tag of an all-encompassing and distinct Hong Kong identity.

Lion Rock Spirit
Lastly, this all-encompassing identity also finds an outlet of expression in the entrepreneuring Lion Rock Spirit, the can-do mentality that drives the common man to fulfil his potential and live a dignified life within China’s special administrative region. Riding their luck and hardship-hardened, the jau gwei make ends meet as small-scale entrepreneurs in the informal food market, thus, ensuring the legacy of the endeared delicacy despite ever-increasing repression by authorities.
In essence, the jau gwei are more than merely merchants. They are the embodiment of a narrative not dissimilar to the American Dream: social mobility through hard-work embedded in liberal entrepreneurism. Hong Kong’s position – and understanding of itself – as an exceptional city carved out on inhospitable rock by exceptional individuals presupposes the city’s entrepreneurial success.
Through this ideal representation of the Lion Rock Spirit, the jau gwei function as a juxtaposition to the ruthless exploitation of unbridled capitalism under pro-Beijing loyalists before, and especially after, a post-Umbrella Movement political landscape. Unlike the property magnates who distribute financial favours amongst themselves to detriment of the general populace, the jau gwei are of the people and authentically cater to the people. A far cry from the plutocratic megalomania exhibited elsewhere.
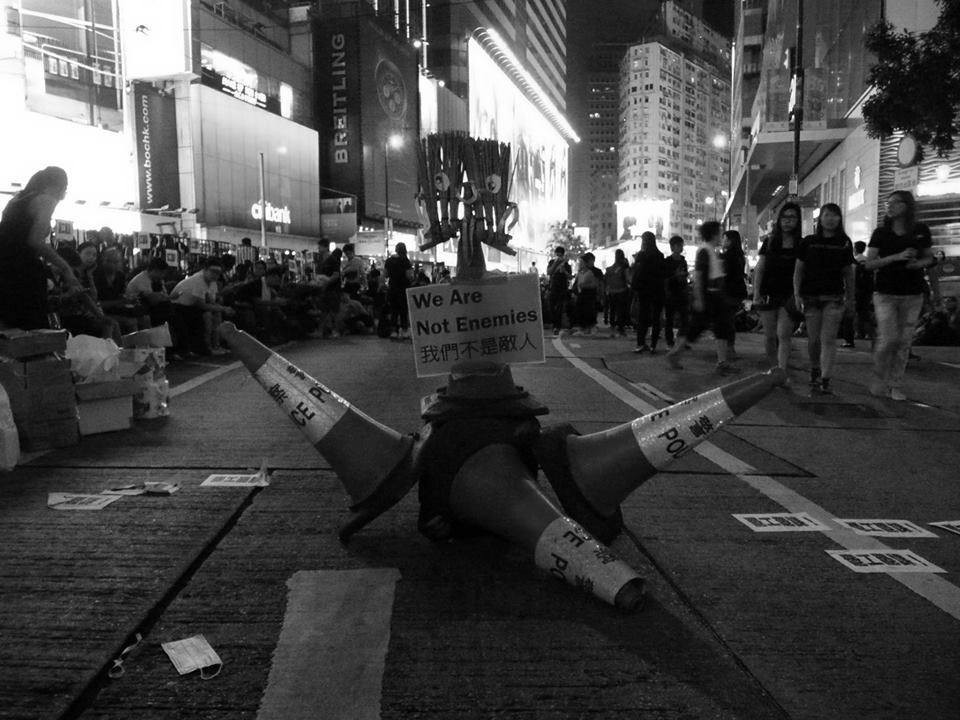

In the crossfire of ideology
In summary, the itinerant hawkers and informal food peddlers beloved by Hong Kongers have found themselves in the crossfire of an ongoing ideological debate over cultural, and therefore inherently political, identity in relation to the legitimacy of the state. In the times of localist and nativist groups demanding a Hong Kong for Hong Kongers (pardon, Chinese, mind you), the jau gwei have come to symbolize something distinctly and peculiarly “of and only from Hong Kong” within the discourse of the legitimacy of the state. Moreover, guided by the small-scale entrepreneurial drive of the individual, the jau gwei signal a juxtaposition to unbridled state capitalism backed by a local pro-Beijing plutocracy, which distributes wealth and power amongst its members.
The narrative of the jau gwei is grinded out somewhere between the tension resulting from the unfair distribution of wealth, power, and politics. To what extent may individual partake take in the distribution thereof before becoming troublesome to the state? As the Mong Kok incident has shown, tensions are running high. As unclear as the future of Hong Kong may be, I venture to say that this analysis hints at these areas of contention within Hong Kong society for future developments in the ongoing crisis.
Written by Louis Louw
Photo Credits
all photos by Michael Wu (instagram: crackerjack_mike), All Rights Reserved