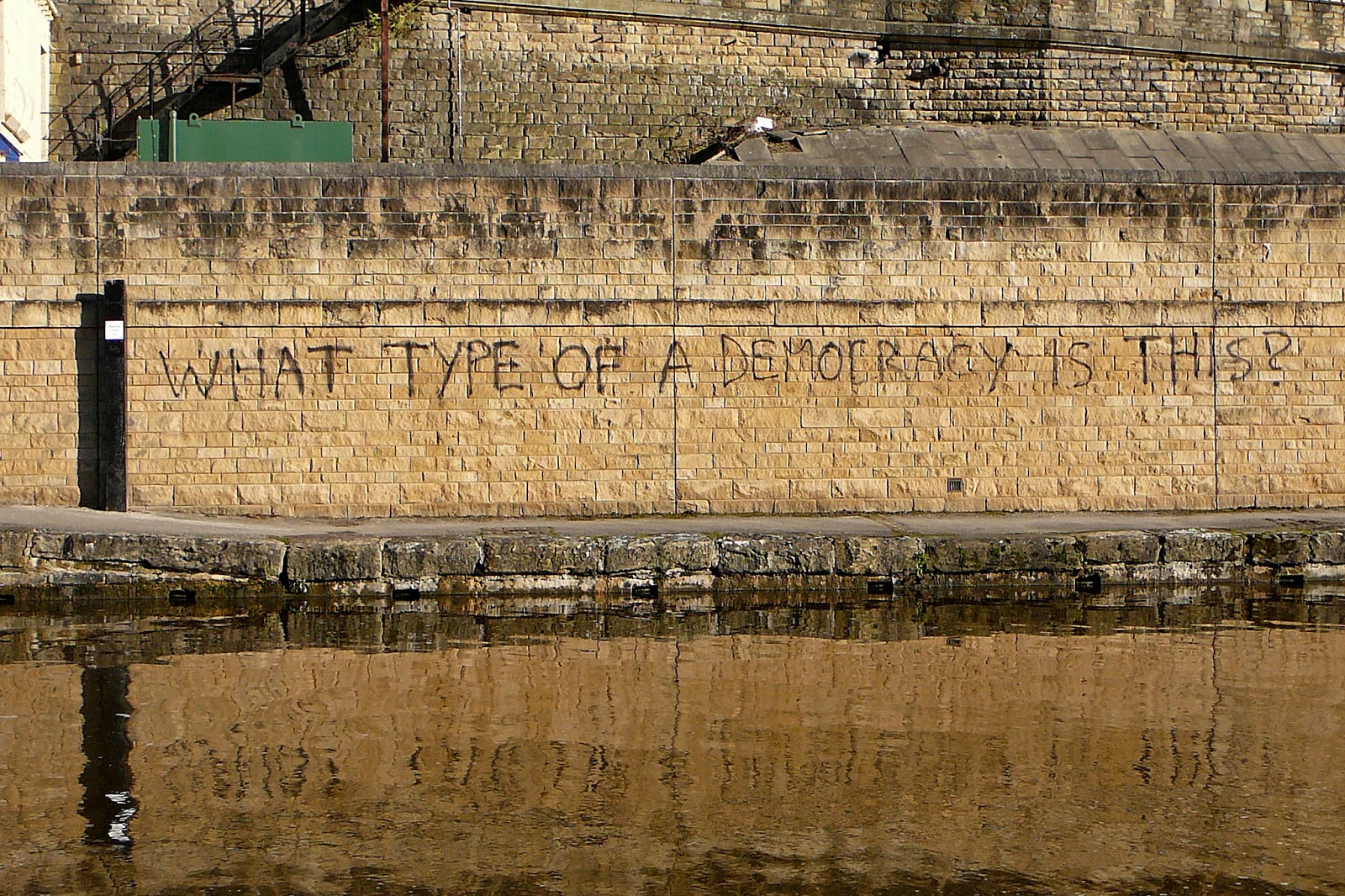It is easy to claim that low voter turnout during elections is due to complacency, indifference and a lazy attitude of taking democratic rights and freedoms that others died, and are still dying, for granted. However, low turnouts, spoilt ballot papers and especially blank votes can be political statements in themselves.
Blank votes and democratic dissatisfaction
Who can be surprised by low turnouts, symptomatic for a lack of confidence in party politics, when policies do not overlap with rhetoric? When elections are presented as an opportunity to evoke positive change but positive change does not come. When the choice offered on the ballot paper seems to be that between plague and cholera. When people feel they need to vote tactically or that their vote does not count due to a winner-takes-it-all system or percentage barriers. Thus, low turnouts don’t necessarily hint at an increasing political indifference in Western society but at an increasing disillusionment with the representative democratic system as it is which makes people turn to informal rather than formal means of political participation.

This trend goes hand in hand with the increasing number of protests as well as blank votes. In the Spanish elections of 2011, 300 000 blank votes (ballot papers that have been left blank), 300 000 spoilt votes (ballot papers that have been filled in or submitted incorrectly) and 100 000 votes for the blank vote party Escaños en blanco (‘blank seats’) were counted which represents about 3 percent of the voters. In the second round of the 2017 French presidential elections 11.52 percent of the ballots cast, more than ever before, where either spoilt (3%) or blank (8.52%). As single cases they hint at the people’s dissatisfaction with the candidates in a specific election, when it becomes a trend it becomes evidence for more fundamental dissatisfaction with the system, says Chiara Superti (Columbia University).
Illusions of democracy
The solution certainly cannot be to brush of all those who do not vote or vote blank as indifferent or even undemocratic. Instead, non-voters, blank votes and spoilt ballot papers can offer insights into citizens’ political opinions. Lessons can be learned from them if we take a step back and reflect on our understanding of democracy.
In The UNESCO Courier sociologist Alain Touraine identifies two prerequisites for democracy: 1) freedom of political choice which makes possible a system in which power is distributed based majority decision, and 2) social conflict, for instance the workers’ movement. Granted, it would be a mistake to adopt a black-and-white thinking in which there exist only democratic and non-democratic systems instead of recognising the multitude of forms and levels of democracy. And, at the same time, if we critically inspect people’s freedom of political choice and democratic representation, we must admit to ourselves that our representative democracy is far from perfect.

In his video on democracy, the YouTuber Oliver Thorn (Philosophy Tube) presented a re-calculation of the Brexit referendum result taking into account the people who were not allowed to vote (prisoners and non-British residents). According to his calculation only 71.2% of the people who have an interest in the UK’s future were allowed to vote on it. Thus, merely 26.6% of the people living in the UK voted to leave the European Union. All debate about Brexit aside, it is fair to say that in this case, as in others, it was not a majority who made a ‘democratic’ decision. And even among those who are able to vote, the majority can overrule the voices of minorities and marginalised groups reducing the democratic system to democracy for the rich and the privileged.
The blank vote
Voting blank as political protest or statement is not a recent phenomenon. It can be traced back to the beginnings of modern Western democracy: in the 1881 French legislative elections around three percent of the votes were voided and in some areas up to 20 percent of the ballot papers were spoilt. Many of the comments that were scribbled on the ballot papers were written in a sophisticated language and showed an understanding of complex political concepts which suggests that the votes had been spoilt as protest based on an informed decision.
However, in many cases blank votes are not taken into consideration. In countries like the UK they are considered spoilt votes. And until recently this was also the case in France. Since 2014 blank votes are counted separately from spoilt votes but have no impact on the election results. Countries like Italy, the Netherlands, Costa Rica and Brazil have the same approach. Blank votes are in these cases merely symbolic. Yet, their recognition would have a real impact on election results. In 1995, Jacques Chirac would not have won the majority in presidential elections, and neither would have François Hollande in 2012, had blank votes been calculated into the election results.
Only few countries recognise the blank vote, and many of them not fully. In Sweden blank votes are only taken into account in referendums. And while Switzerland recognises blank votes, they merely have a noticeable impact in certain local elections since a relative majority is sufficient to win the presidential elections. In Spain blank votes are taken into consideration when calculating the participation threshold, yet only valid ballot papers are used to calculate the seat distribution in parliament. It is in Latin America where we can find countries that fully recognise the blank vote. In Colombia blank votes can invalidate an election making it necessary to repeat it. This second round, however, cannot be invalidated. Likewise, in Peru blank votes can bring about a repetition of the elections if they represent two thirds of the votes.
Recognising the blank vote
While the recognition of the blank vote might lead to voters favouring rejection over approval votes and a high number of blank votes might result in a political crisis, it can benefit democracy in many ways. It would not only better reflect the political will and opinion of the voters but might also lead to higher turnouts. The option of voting blank would provide additional incentive for politicians to present election programmes and policies that convince the voters rather than presenting nothing more than the lesser of two evils.
In countries like Italy, Chile and Colombia, Chiara Superti argues, often more votes are cast blank than are given to many minor or extreme parties that are generally considered the choice of protest voters. Politicians should see the blank vote as a sign of the people’s discontent before it augments to a level that erupts in widespread protests, says Olivier Durand, founding president of the Association pour la reconnaissance du vote blanc. He promotes the adoption of a system of recognition of blank votes in which a certain percentage of blank votes would lead to a third round in the French presidential elections with different candidates.

The debate on the recognition of the blank vote in France reemerged in the context of the Gilets jaunes movement. But its history predates the recent wave of protests. Since 1958 there have been 60 law drafts concerning the blank vote. In 2017, seven presidential candidates expressed their support for its recognition. And only Emmanuel Macron (La République en Marche), François Fillion (Les Républicains), Marine Le Pen (Rassemblement National) and Philippe Poutou (Nouveau Parti anticapitaliste) did not mention the blank vote in their election programmes.
The recognition of the blank vote might make elections more complex and complicated. Yet it might also make our democracies more democratic. And no matter which side we take in the debate on the blank vote, there is one thing at least that we can learn from it: democracy is not singular. Democracy contains multitudes of different forms and levels of democracy. It lives of constructive debates that do not hold on to the current form of democracy as the one truth, the ultimate democratic achievement but that are open to change in order to improve lived democracy.
by Merle Emrich
Photo Credits
What type of a democracy…, Tim Green, CC BY 2.0
Democracy, Nico Hogg, CC BY-NC 2.0
Brexit, Ungry Young Man, CC BY 2.0